
The alchemists' dream came true: they managed to transform lead into gold
The ALICE experiment at CERN managed to turn lead into gold, but the result is almost impossible to exploit
For centuries, alchemy dreamed of turning lead into gold. That old desire, a mix of science and mysticism, finally became a reality. But the result is far from what ancient laboratories imagined.
An experiment at the Large Hadron Collider, the world's most powerful particle accelerator, managed to transform lead atoms into gold. However: there is a key condition that prevents this process from having economic value.
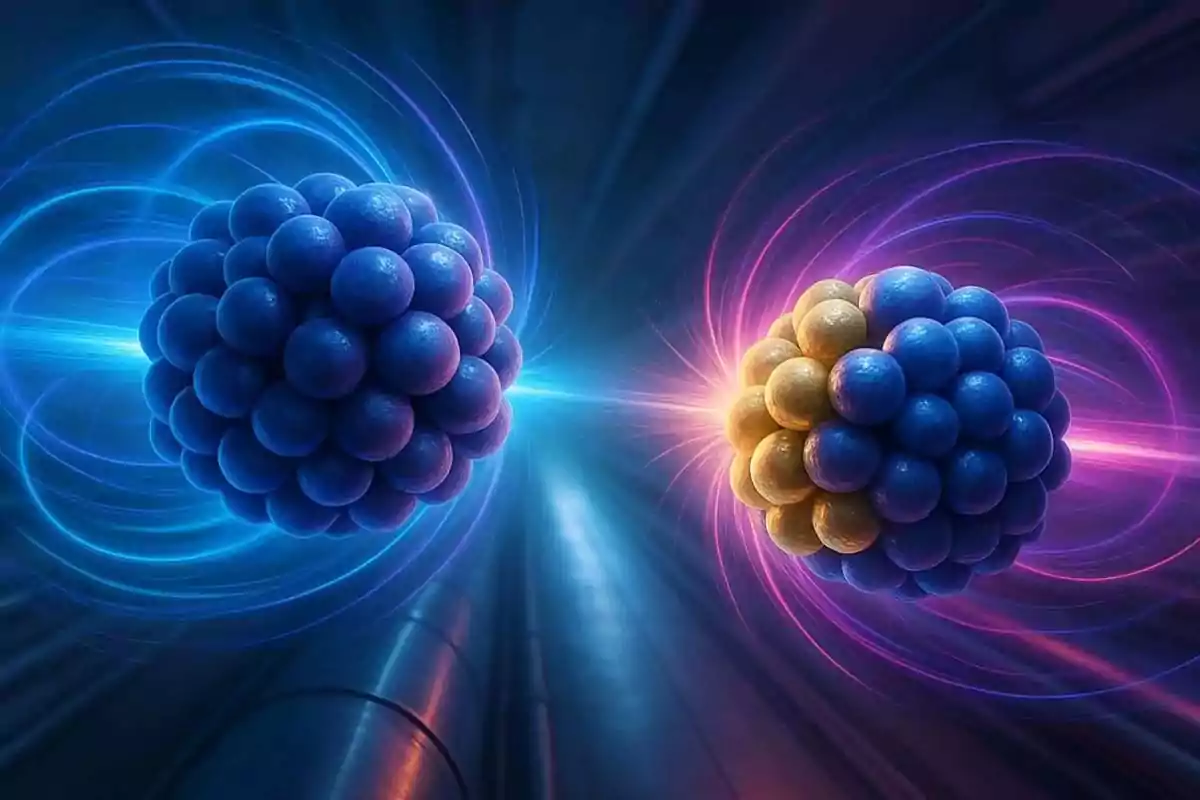
How did they transform lead into gold at CERN?
The discovery occurred within the framework of the ALICE experiment, one of the projects of the Large Hadron Collider, located on the outskirts of Geneva. In this 27-kilometer underground ring, lead nuclei are launched at speeds close to light.
When two nuclei graze each other, their electromagnetic fields generate an extreme reaction. That friction strips protons from the nucleus, changing its atomic structure.
What happens when protons are lost?
- Lead has 82 protons.
- If it loses three, it transforms into gold (79 protons).
- If it loses one or two, it becomes thallium or mercury, respectively.
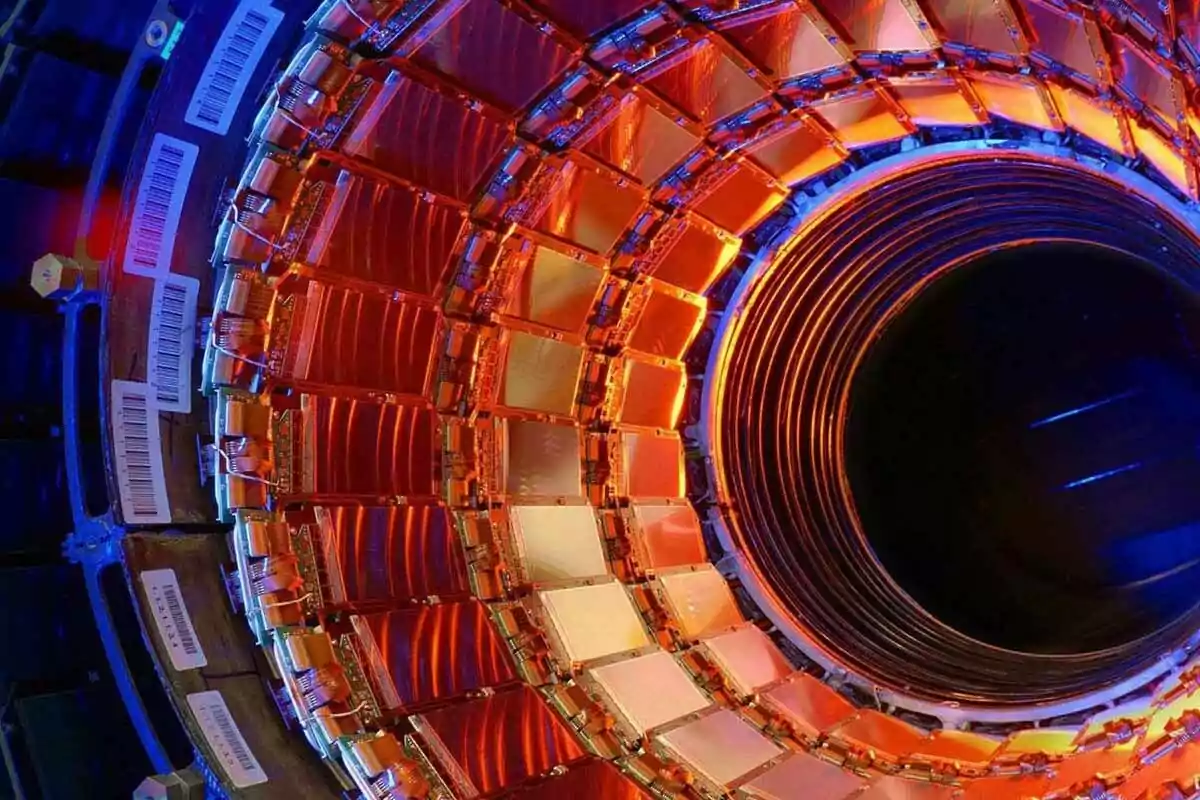
To confirm this conversion, scientists used zero-degree calorimeters, ultrasensitive detectors developed by Italy's INFN.
How much gold did they manage to create?
Between 2015 and 2018, the ALICE team managed to generate about 86 billion gold nuclei. It may sound like a lot, but the total amount is minuscule.

All that gold together weighs just 29 millionths of a millionth of a gram. That is, impossible to see, touch, or accumulate.
Why can't that gold be utilized?
Because it doesn't last. The gold nuclei that form are destroyed almost immediately. According to CERN, upon exiting the collision, they travel with so much energy that they collide with the beam tube or collimators and fragment.
"The gold only exists for a tiny fraction of a second," explained the scientific body. As it disintegrates, it turns back into protons, neutrons, and smaller particles.

What does this experiment mean for science?
The transmutation dreamed of by alchemists is now a fact. Although it doesn't serve to create jewelry or ingots, it demonstrates that transforming one element into another is possible with the right technology.
In the words of the CERN team: "Technically, the dream is a reality, but getting rich this way remains a chimera."
More posts: